 |
Washington DC (SPX) Sep 20, 2010 Enjoying a frozen treat on a hot summer day can leave a sticky mess as it melts in the Sun and deforms. In the cold vacuum of space, there is no edible ice cream, but there is radiation from massive stars that is carving away at cold molecular clouds, creating bizarre, fantasy-like structures. These one-light-year-tall pillars of cold hydrogen and dust, imaged by the Hubble Space Telescope, are located in the Carina Nebula. Violent stellar winds and powerful radiation from massive stars are sculpting the surrounding nebula. Inside the dense structures, new stars may be born. This image of dust pillars in the Carina Nebula is a composite of 2005 observations taken of the region in hydrogen light (light emitted by hydrogen atoms) along with 2010 observations taken in oxygen light (light emitted by oxygen atoms), both times with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys. The immense Carina Nebula is an estimated 7,500 light-years away in the southern constellation Carina. The Hubble Space Telescope is a project of international cooperation between NASA and the European Space Agency. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center manages the telescope. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) conducts Hubble science operations. STScI is operated for NASA by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. in Washington, D.C.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) Stellar Chemistry, The Universe And All Within It
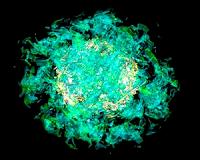 3-D Computer Simulations Help Envision Supernovae Explosions
3-D Computer Simulations Help Envision Supernovae ExplosionsPrinceton NJ (SPX) Sep 17, 2010 For scientists, supernovae are true superstars - massive explosions of huge, dying stars that shine light on the shape and fate of the universe. For a brief burst of time, supernovae can radiate more energy than the sun will emit in its lifetime. With the potential energy of 25 hundred trillion trillion nuclear weapons, they can outshine entire galaxies, producing some of the biggest explo ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |