 |
London, UK (SPX) Mar 29, 2011 The earliest rocks in our Solar System were more like candy floss than the hard rock that we know today, according to research published in the journal Nature Geoscience. The work, by researchers from Imperial College London and other international institutions, provides the first geological evidence to support previous theories, based on computer models and lab experiments, about how the earliest rocks were formed. The study adds weight to the idea that the first solid material in the Solar System was fragile and extremely porous - much like candy floss - and that it was compacted during periods of extreme turbulence into harder rock, forming the building blocks that paved the way for planets like Earth. Dr Phil Bland, lead author of the study from the Department of Earth Science and Engineering at Imperial College London, says: "Our study makes us even more convinced than before that the early carbonaceous chondrite rocks were shaped by the turbulent nebula through which they travelled billions of years ago, in much the same way that pebbles in a river are altered when subjected to high turbulence in the water. Our research suggests that the turbulence caused these early particles to compact and harden over time to form the first tiny rocks." The researchers reached their conclusions after carrying out an extremely detailed analysis of an asteroid fragment known as a carbonaceous chondrite meteorite, which came from the asteroid belt between Jupiter and Mars. It was originally formed in the early Solar System when microscopic dust particles collided with one another and stuck together, coalescing around larger grain particles called chondrules, which were around a millimetre in size. To analyse the carbonaceous chondrite sample, the team used an electron back-scatter defraction technique, which fires electrons at the sample. Researchers observe the resulting interference pattern using a microscope to study the structures within. This technique enabled the researchers to study the orientation and position of individual micrometre-sized grain particles that had coalesced around the chondrule. They found that the grains coated the chondrule in a uniform pattern, which they deduced could only occur if this tiny rock was subjected to shocks in space, possibly during these periods of turbulence. The team also defined a new method to quantify the amount of compression that the rock had experienced and deduce the rock's original fragile structure. Dr Bland adds: "What's exciting about this approach is that it allows us - for the first time - to quantitatively reconstruct the accretion and impact history of the most primitive solar system materials in great detail. Our work is another step in the process helping us to see how rocky planets and moons that make up parts of our Solar System came into being." In the future, the team will focus further studies on how the earliest asteroids were built.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Imperial College London Stellar Chemistry, The Universe And All Within It
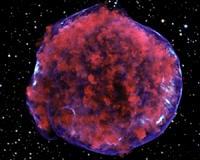 Exploding Stars And Stripes
Exploding Stars And StripesWashington DC (SPX) Mar 25, 2011 The discovery of a pattern of X-ray "stripes" in the remains of an exploded star may provide the first direct evidence that a cosmic event can accelerate particles to energies a hundred times higher than achieved by the most powerful particle accelerator on Earth. This result comes from a very long observation of the Tycho supernova remnant with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. It could e ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |