 |
Gainesville FL (SPX) Feb 26, 2007 A new study provides evidence that the last inhabitants of Christopher Columbus� first settlement desperately tried to extract silver from lead ore, originally brought from Spain for other uses, just before abandoning the failed mining operation in 1498. It is the first known European extraction of silver in the New World. University of Florida archaeologist Kathleen Deagan co-authored the study and led the fieldwork at La Isabela, founded in 1493 on modern day Dominican Republic�s north coast. Deagan collaborated with geoscientists and metallurgists to interpret a smelting operation at the site that appeared to have used nearly 200 pounds of galena, a silver-bearing lead ore. Findings will be published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Feb. 27 print edition. �We first thought they mined the galena locally to extract lead for weapons, such as lead shot and musket balls or ship sheathing,� said Deagan, a distinguished research curator at the Florida Museum of Natural History. �But an isotope analysis showed it was actually from Spain. And metallurgical analysis shows they were trying to extract silver. The archaeological evidence suggested just how desperate the last settlers at the colony were to get precious metal before abandoning the settlement.� Columbus established La Isabela on his second expedition, which Deagan says was a quest for precious metals. Mining and metallurgy were central elements to the settlement of about 1,500 people � almost all men. �Columbus really expected and needed to find gold,� she said. �Anytime we recovered evidence for metallurgy � like ore, slag or equipment for smelting � it was important.� Deagan and her team excavated the galena inside a structure they identified as the royal storehouse, near the front entry. Just outside the entry, they excavated more than 440 pounds of metal slag material. Deagan said it was associated with a fire pit likely used for heating metals. �All the galena was in the last stratigraphic layer of the storehouse,� Deagan said. �The smelting was one of the last activities to take place.� Deagan collaborated with other researchers to understand how the settlers processed the materials. She contacted archaeometallurgist David Killick at the University of Arizona and provided samples and funding for his laboratory. Alyson Thibodeau, a geosciences graduate student working with Killick and lead author of the paper, performed an isotope analysis. �We found that the samples from La Isabela were extremely consistent with galena found in Spain near the port where the second expedition sailed from,� Thibodeau said. Deagan was surprised to learn the galena was not mined locally. �So the question was: Why did they haul this heavy, unrefined lead ore all the way from Spain when they could have brought processed lead?� Deagan said. By consulting with Spanish experts in medieval metallurgy, the team discovered other past uses for galena. In medieval times, they learned, galena was used as flux to draw precious metals from ore matrices and to test their purity. This is likely how La Isabela�s settlers used it. Killick pieced together the settler�s unconventional use of the galena when he identified the excavated slag as lead silicate � the end product of an improvised smelting process. He discovered tiny specks of silver upon examining the lead silicate with optical and scanning electron microscopy. �That�s when the penny dropped,� he said. �I realized they were wasting all the lead trying to separate out the silver.� Deagan said the metal analysis showed the settlers didn�t quite know what they were doing. �They were clearly trying to get the silver out of it,� Deagan said. �But the byproducts showed they had too much of one chemical, but not enough of another. Someone knew a little bit, but not enough.� Ann Ramenofsky, an archaeologist at the University of New Mexico, reviewed the study. �Given there was someone on the expedition who knew how to do these extractions suggests metallurgy was significant, even though Isabela ultimately failed,� Ramenofsky said. �Deagan deserves high praise for a beautiful excavation. It�s changed our understanding of the Spanish conquest of the Americas.� Related Links University of Florida All About Human Beings and How We Got To Be Here Powering The World in the 21st Century at Energy-Daily.com Our Polluted World and Cleaning It Up All About Human Beings and How We Got To Be Here
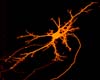 Bethesda MD (SPX) Mar 12, 2007
Bethesda MD (SPX) Mar 12, 2007Here is some news that will certainly get on people's nerves: In a study to be published in the March 2007 issue of The FASEB Journal, scientists from East Carolina University report that a key molecular mechanism, RNA interference (RNAi), plays a role in the regeneration and repair of periphery nerves, which are the nerves located outside of the brain and spinal column. |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright Space.TV Corporation. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement, agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by Space.TV Corp on any Web page published or hosted by Space.TV Corp. Privacy Statement |