 |
Washington DC (SPX) Aug 06, 2010 A beautiful new image of two colliding galaxies has been released by NASA's Great Observatories. The Antennae galaxies, located about 62 million light years from Earth, are shown in this composite image from the Chandra X-ray Observatory (blue), the Hubble Space Telescope (gold), and the Spitzer Space Telescope (red). The collision, which began more than 100 million years ago and is still occurring, has triggered the formation of millions of stars in clouds of dusts and gas in the galaxies. The most massive of these young stars have already sped through their evolution in a few million years and exploded as supernovas. The X-ray image from Chandra shows huge clouds of hot, interstellar gas that have been injected with rich deposits of elements from supernova explosions. This enriched gas, which includes elements such as oxygen, iron, magnesium and silicon, will be incorporated into new generations of stars and planets. The bright, point-like sources in the image are produced by material falling onto black holes and neutron stars that are remnants of the massive stars. Some of these black holes may have masses that are almost one hundred times that of the Sun. The Spitzer data show infrared light from warm dust clouds that have been heated by newborn stars, with the brightest clouds lying in the overlap region between the two galaxies. The Hubble data reveal old stars in red, filaments of dust in brown and star-forming regions in yellow and white. Many of the fainter objects in the optical image are clusters containing thousands of stars. The Antennae galaxies take their name from the long antenna-like "arms," seen in wide-angle views of the system. These features were produced by tidal forces generated in the collision.
Share This Article With Planet Earth
Related Links Spitzer Space Telescope Stellar Chemistry, The Universe And All Within It
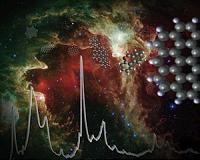 NASA Reveals Key To Unlock Mysterious Red Glow In Space
NASA Reveals Key To Unlock Mysterious Red Glow In SpaceMoffett Field CA (SPX) Aug 04, 2010 NASA scientists created a unique collection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) spectra to interpret mysterious emission from space. Because PAHs are a major product of combustion, remain in the environment, and are carcinogenic, the value of this PAH spectral collection extends far beyond NASA and astronomical applications. For years, scientists have been studying a mysterious infrar ... read more |
|
| The content herein, unless otherwise known to be public domain, are Copyright 1995-2010 - SpaceDaily. AFP and UPI Wire Stories are copyright Agence France-Presse and United Press International. ESA Portal Reports are copyright European Space Agency. All NASA sourced material is public domain. Additional copyrights may apply in whole or part to other bona fide parties. Advertising does not imply endorsement,agreement or approval of any opinions, statements or information provided by SpaceDaily on any Web page published or hosted by SpaceDaily. Privacy Statement |